You are here
Reduce Emissions from Energy Consumption (Ongoing)
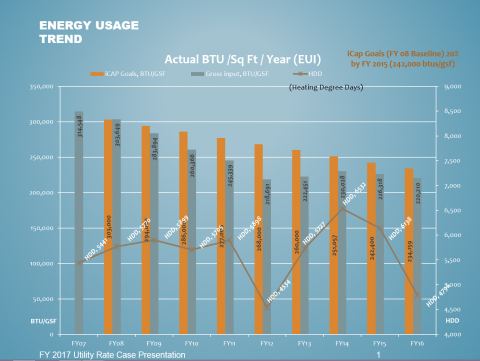
As of the metrics available for FY14, 88% of our greenhouse gas emissions result from on-site combustion and grid electricity purchases that heat, cool, and provide electricity to campus buildings. Consequently, achieving our carbon neutrality goal will require both a strong building energy conservation program and also a shift in our energy generation and purchasing towards renewable sources. While both of these elements are critical and must be pursued by our campus, energy conservation is considered to be a top priority as it leads directly to both emissions reductions and cost savings that can facilitate even further emission reductions.
Emission Factors
As of FY14, the emission factors for the following forms of energy used on campus are as follows:
- Electricity: 0.821 kg CO2 / kWh
- Propane: 5.22 kg CO2 / gallon
- Steam: 28.9 kg CO2/ 1000 pounds of steam
Sub-projects
-
 (Ongoing)
(Ongoing) -
 (Ongoing)
(Ongoing)
Background
Metrics
Carbon Emissions from Energy (MTE)
Total Annual Energy Consumption
Annotations
- FY 2005:
1 Million MMBTU’s is one million million mmbtus, or one trillion BTUs. 1 x 10^12.
Total Coal Use at Abbott Power Plant (MMBTU)
Total Electric Usage for all of campus in kilowatt-hours (kWh)
Total Natural Gas Use (MMBTU)
Recent Project Updates
-
3/24/2025Mike Larson, director of utility operations at the Abbott Power Plant described UIUC's Campus Chilled Water System (CCWS) at the 2025 Chief Engineers & Facility Managers Conference. Software and hardware upgrades were made to the CCWS ...
-
4/4/2023Hi Rob, Do we have an updated chart to show the progress to date, i.e. FY22.Ehab--------------------------------Morgan – Is this your chart?Rob Roman-------------------------------Hi Rob, It is from the icap portal at https://...
Themes
-
Primary Theme:
